(Ⅰ) Die casting machine
In the case of die casting equipment planning, priority should be given to the die casting machine which is the main device. After the machine is selected according to the specifications of product to be produced, corresponding auxiliary equipment can be confirmed. There are still several points that should be noticed after the die casting machine is finalized.
1. Consider whether the mold can be mounted on the machine successfully. Think about whether the core pulling cylinder would conflict with other parts when the mold has more cores.
2. Consider the injection position. General die casting machines have one or two injection positions and the layout of injection holes should be noticed as well. For example, the user manual says “0, -250”which usually means the position of 0 and -250 rather than the range between 0 to -250. Therefore the user should be careful and avoid misunderstanding the instruction.
3. Consider whether location and specifications of the standard T-slot are suitable for the mold, especially the one with the core pulling cylinder. As the hydraulic automatic die clamp may be mounted in the T-slot, it should be noted that whether the core pulling cylinder interferes with the die clamp.
4. Pay attention to whether the ejection holes of the moving platen meet the requirements of ejection.
5. Pay attention to the integration and universality of injection components such as the injection chamber, plunger and plunger rod.
6. Think about whether the quantity of core pulling is enough.
7. Think about the quantity of cooling water switch is enough especially when the cooling water channels are complicated.
(Ⅱ) Furnace
After the die casting machine is confirmed, the furnace that provides liquid aluminum to the die casting machine should be selected. There are different kinds of furnaces that have various functions and use different resources. At present, natural-gas- based and electricity-based furnaces are the most popular and environment-friendly. When there are a large number of die casting machines and the liquid aluminum is in a great demand, it is suggested that centralized melting and machine-side holding should be used. Otherwise, when the quantity of machines is small and the liquid aluminum is less required, it is recommended that the machine-side melting and holding furnace should be used. Specifications of furnaces for corresponding machine models are listed below:
|
No. |
Machine |
Quantity of Aluminum |
Furnace |
Notes |
|
1 |
140T-180T |
80Kg/h |
300 Kg |
|
|
2 |
300T-400T |
100 Kg/h |
500 Kg |
|
|
3 |
500T |
130 Kg/h |
600-700 Kg |
|
|
4 |
650T-800T |
180-220 Kg/h |
800-1000 Kg |
|
|
5 |
900T-1000T |
280-300 Kg/h |
1000-1200 Kg |
|
|
6 |
1250T |
400 Kg/h |
1200-1500 Kg |
|
|
7 |
1650T |
450-500 Kg/h |
1500-2000 Kg |
|
|
8 |
2000T |
550 Kg/h |
2000 Kg |
|
|
9 |
2500T-3000T |
≥600 Kg/h |
≥2000 Kg |
Depending on the product |
After the specifications of furnace are confirmed, the feeding opening of furnace, the height of tap hole and the ladling device should be considered.
(Ⅲ) Ladling equipment
In early die casting production, a ladle of molten metal is scooped and poured into the barrel of die casting machine, which results in high labor intensity and various quality of ladling. Now the ladling device is upgraded and becomes automatic. There are four kinds of ladles: (1) single-arm ladle (Fig. 2), (2) five-pivot-point ladle (Fig. 3); (3) overhead ladle (Fig. 4); (4) ladling robot (Fig. 5).
Single-arm ladle is simply chain-structure-based and widely used early. Due to necessary frequent maintenance, the single-arm ladle is gradually replaced by five-pivot-point ladle which is more smooth and stable than the predecessor. The overhead ladle usually works with large-scale die-casting machines such as 1650T machine and larger ones. The overhead ladle can smoothly scoop larger quantity of molten aluminum, but it costs more in manufacturing compared with the five-pivot-point ladle and occupies more space. Therefore, the five-pivot-point ladle now is more popular and domestic case of using ladling robot is rare.


Figure 2 Figure 3
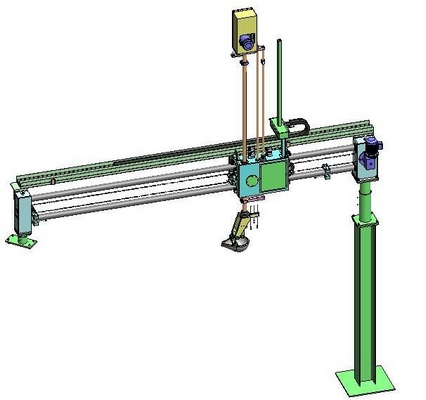
Figure 4
(Ⅳ) Spraying equipment
More and more automatic spraying equipment is widely used instead of the manual spray gun that cannot always ensure high-quality spraying. Common spraying machines are listed below:
(1) Vertical rotary sprayer that adopts the brass spray head and is mainly used in the 140-900T die casting machines. See figure 6.
(2) Multi-linkage sprayer that usually adopts the brass spray head and is mainly used for large tonnage die casting machines over 1000T. See figure 7.
(3) Servo sprayer that usually adopts nozzle structure and is mainly used for spray coating of deep-cavity product. This sprayer is suitable for all machine models, but the robotic spray system is more often applied to the machines over 1650T.
(4) Robotic spray system that usually adopts a nozzle-type structure and is mainly applied to machines over 1000T, especially the ones over 1650T. The robot is flexible and its nozzle is suitable for molds of different specifications. See figure 9.



Figure 5 Figure 6 Figure 7
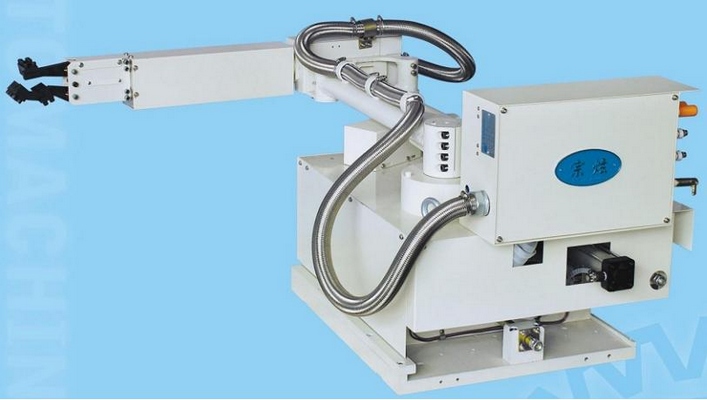



Figure 8 Figure 9 Figure 10
(Ⅴ) Extraction equipmentIn the past, the die cast parts are take out by the operator with a clamp, which was dangerous and required great strength. Now die cast part extraction is done by automatic extraction equipment that has two common varieties.
(1) Automatic extractor that is usually applied to machines less than 1000T can be driven by cylinder (see figure 10) or motor (see figure 11). The cylinder-driven extractor was more common in the past and now it is gradually replaced by the motor-driven one that works faster and more smoothly.
(2) Robotic extraction system is often used in operation of high-level automation. The six-axis robot with tongs can extract die cast parts and work with other auxiliary equipment for other processing procedures. This extraction system is suitable for die casting machines over 650T. See figure 13.
(Ⅵ) Casting integrity check
To judge weather the die cast parts are taken out completely, the scumriser will be checked by two collision-type inductive switches or 4 to 8 photoelectric detectors (see figure 14). The casting integrity test device is usually contained in the extraction equipment.
(Ⅶ) Release agent mixer
This device provides the spraying equipment with a good proportion of mold release agent. The quantity and specifications of the mixer depend on the quantity of die casting machine. When selecting the mixer, the capacity of the original liquid barrel, mixed liquid barrel and the pump should be considered as well. See figure 15.
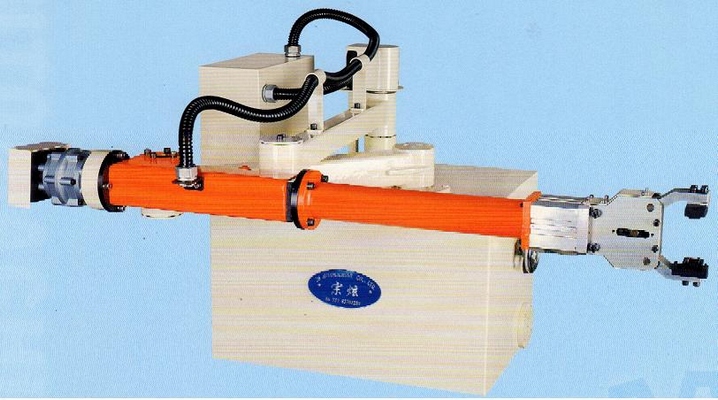



Figure 11 Figure 12 Figure 13
(Ⅷ) Conveyor
The castings taken out by the extractor are placed on the conveyor that is equipped with two to three cooling fans. The castings are transferred one side to the other for further process. For 140-900T die casting machines, the effective width of conveyor belt usually ranges from 0.4-0.6m; for 1000-3000T machines, the belt width is 0.8-1.2m. See figure 16.



Figure 14 Figure 15 Figure 16
(Ⅸ) Cooling water bath
If the extractor robot is part of the automatic die casting unit, there will be the procedures below:
(1) The robot grips the casting and dips it into the bath for cooling.
(2) The water bath is equipped with the clamp that holds the casting firmly for cooling. The robot will take the casting away from the bath when it completes other procedures.
There is an inlet at the bath bottom where a solenoid valve is mounted and an outlet at the upper bath. A temperature sensor is mounted in the water bath. When the water temperature is beyond the setting, the solenoid valve at the inlet turns on; the cooling water flows in; the excessive hot water flows out until the temperature is within the setting and then the solenoid valve turns off. See figure 17.
(Ⅹ) Quick die change device
For die casting machine that often undergoes changeover of die, using the hydraulic automatic mold clamp instead of manual mold clamp will considerably improve the efficiency of mold changing. The die is held firmly or loosened by pressing the button. See figure 18.
(Ⅺ) Coding machine
This device marks the die cast part with identification code to facilitate quality tracking in the future. The castings are generally held by the machine or special clamp for marking. There are dot matrix printing and laser printing. As the latter is expensive, dot matrix printing is actually used more often. See figure 19.
(Ⅻ) Skim bob removing device
In the die casting unit consisted of the robotic extraction system, if the skim bob of die cast part is removed by collision, a support with several adjustable stop blocks is needed (see figure 20). The robot will perform actions under the control of pre-set program, clamp the die cast part and make the skim bob collide with the stop block for removal.



Figure 17 Figure 18 Figure 19
(XIII) Trimming machineThe trimming machine is used to cut the runner and skim bob of the die cast parts (see figure 21). For satisfactory processing effect, the trimming die should meet certain strict requirements. Many die cast manufacturers have purchased trimming machines but their role weakened due to the unqualified trimming die.
(XIV) Mold temperature control equipment
The mold temperature controller (see figure 22) is mainly used in die casting of magnesium alloy because forming of this kind of die castings is closely related to temperature. Sometimes the mold temperature controller is also applied in the forming of aluminum alloy die castings that have complicated shapes and high requirements. Selection of the temperature controlling machine depends on the complexity, sometimes the temperature requirement of the die. Considerations include the power of pump, heating power, and the number of working circuit of mold temperature. Single-loop is generally used in single mold temperature control; double-loop is generally used in double-mold-temperature control. (Temperature requirements of movable die half and fixed die half differ.)
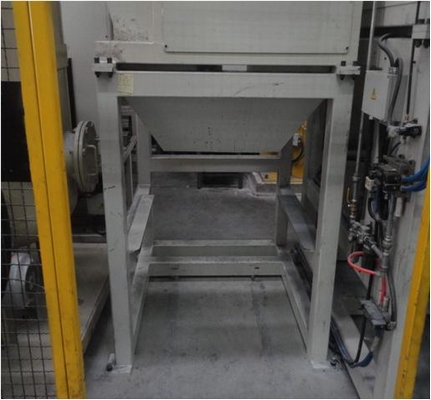



Figure 20 Figure 21 Figure 22
(XV) Vacuum machineVacuum die casting is usually used to produce highly demanding die casting parts. First, the high-quality vacuum die is required. Then a vacuum valve that is connected to the vacuum machine is mounted on the die (see figure 23). The vacuum valve turns on before the liquid aluminum enters the cavity so that the vacuum machine withdraws the air in the die and the cavity has a certain degree of vacuum. The vacuum valve will turn off after the liquid aluminum enters the cavity and the forming of die casting begins.
(XVI) Work station and safety fences
For die casting machines, especially large-tonnage machines over 1000T, that are equipped with a number of auxiliary devices, the work station is usually designed and made at the operation side for safety and convenient operation excluding the condition that the height of factory is not enough or the ground subsides. Safety fences also should be used at the non-operation side to fence off the extraction robot and other auxiliary equipment. A safety gate with the bolt should be installed at an appropriate location so that the die casing unit stops working once the safety gate is opened.
The die casting manufacturers can select the auxiliary equipment above according to the actual production conditions so as to facilitate high-quality, high-efficiency automatic production.


Figure 23 Figure 24